Complete Bike Fitting Guide | Pro Tips & Calculator Tools
A proper bike fit is essential for comfort, efficiency, and injury prevention. This comprehensive guide will walk you through professional bike fitting techniques, whether you're a beginner getting your first bike or an experienced cyclist looking to optimize your position using precise measurements and calculations.
Quick Answer: Use the 109% inseam method for saddle height, ensure 25-35° knee bend, and maintain proper weight distribution (60% rear, 40% front) for optimal bike fit. Our Bike Size Calculator provides personalized measurements.
Table of Contents
- Why Proper Bike Fit Matters
- Understanding Bike Geometry
- Essential Bike Fit Measurements
- Saddle Height Calculator Guide
- Saddle Positioning Techniques
- Handlebar Fit Optimization
- Professional Bike Fitting Options
- Common Fit Problems & Solutions
- FAQ: Bike Fitting Questions
Specialized Bike Fitting Tools
For optimal bike fitting, use our specialized calculators designed for different bike types:
- Kids Bike Size Calculator: Age-appropriate sizing for growing children
- Mountain Bike Size Calculator: Trail-specific geometry and standover clearance
- Road Bike Size Calculator: Performance-oriented sizing for speed and efficiency
- Saddle Size Calculator: Perfect saddle width based on sit bone measurements
- Stem Length Calculator: Optimal reach and handling positioning
Each calculator provides bike-type-specific recommendations to complement the general fitting principles in this guide.
The Importance of Proper Bike Fit
Professional Bike Fitting Benefits
A proper bike fitting using professional techniques and measurements can:
- Increase comfort on long rides by 40-60%
- Improve power transfer and pedaling efficiency by up to 15%
- Reduce the risk of overuse injuries and repetitive strain
- Enhance bike handling and control through proper weight distribution
- Prevent numbness and tingling in hands and feet
- Minimize muscle fatigue during extended rides
- Optimize breathing and aerodynamics for performance
- Improve overall riding experience and confidence
Bike Fit Calculator Tip
Your bike fit may change over time as your flexibility, strength, and riding style evolve. Use our Bike Size Calculator to reassess your measurements periodically, especially after any significant changes in your fitness level or if you experience discomfort during rides.
Understanding Bike Geometry
Before diving into specific measurements, it's important to understand basic bike geometry and how it affects your riding position:
Frame Geometry
- Stack height: The vertical distance from the bottom bracket to the top of the head tube
- Reach: The horizontal distance from the bottom bracket to the head tube
- Head tube angle: Affects handling characteristics and front-end geometry
- Seat tube angle: Influences your position relative to the bottom bracket
- Wheelbase: Impacts bike stability and maneuverability
How Geometry Affects Fit
Different riding styles require different geometries:
- Race bikes typically have aggressive geometries with longer reach and lower stack
- Endurance bikes feature more relaxed geometries with shorter reach and taller stack
- Touring bikes prioritize stability with longer wheelbases and relaxed angles
- Mountain bikes need specific considerations for trail riding - learn more in our Mountain Bike Sizing Guide
- Kids' bikes require age-appropriate sizing principles - see our Kids Bike Sizing Guide
Basic Bike Fit Measurements
There are several key measurements to consider when fitting a bike:
- Saddle height - Affects knee extension and power
- Saddle fore/aft position - Affects weight distribution and pedaling mechanics
- Reach to handlebars - Affects upper body comfort and handling
- Handlebar height - Affects back angle and aerodynamics
- Cleat position - Affects foot alignment and power transfer

Setting Saddle Height
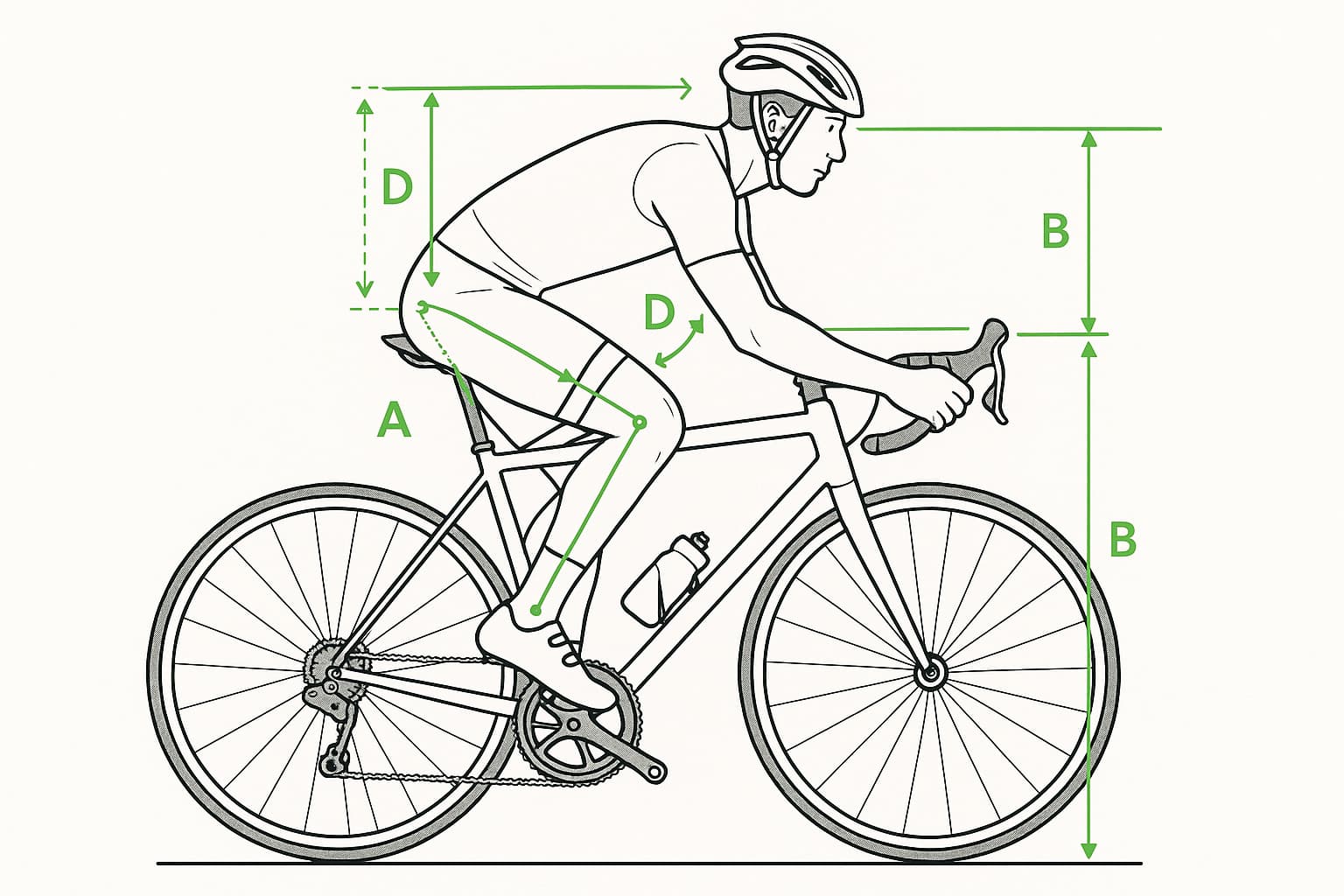
The saddle height is perhaps the most critical aspect of bike fit. A saddle that's too high or too low can cause knee pain and reduce pedaling efficiency.
The 109% Method (Inseam Calculator)
The most reliable starting point for saddle height calculation:
- Measure your inseam in centimeters (barefoot, back against wall)
- Multiply by 1.09 (some riders prefer 1.08-1.10)
- Measure from bottom bracket center to the top of your saddle
- Fine-tune based on comfort and pedaling efficiency
Example: 80cm inseam × 1.09 = 87.2cm saddle height
Our Bike Size Calculator includes an advanced inseam calculator for precise measurements.
The Heel Method
- Sit on your bike while leaning against a wall or on a trainer
- Place your heel on the pedal at its lowest position
- Your leg should be straight but not locked
- When you place the ball of your foot on the pedal, you'll have the proper slight bend in your knee
Fine-Tuning Saddle Height
Consider these factors when fine-tuning your saddle height:
- Aim for a knee bend of 25-35 degrees at the bottom of the pedal stroke
- Watch for hip rocking, which indicates the saddle is too high
- Pay attention to any knee pain: anterior (front) pain often means the saddle is too low, while posterior (back) pain suggests it's too high
- Account for cleat stack height and shoe thickness
Visit our Saddle Size Calculator for a personalized saddle height recommendation based on your inseam measurements and riding style.
Saddle Fore/Aft Position
The fore/aft position of your saddle is crucial for proper weight distribution and efficient pedaling.
Setting Fore/Aft Position
- KOPS Method (Knee Over Pedal Spindle)
- While seated with cranks horizontal
- Drop a plumb line from the front of your knee
- The line should intersect the pedal spindle
- Weight Distribution
- Typically aim for 60% rear, 40% front weight distribution
- May vary based on riding style and discipline
Saddle Tilt
- Start with the saddle perfectly level
- Minor adjustments of 1-2 degrees may help with comfort
- Avoid excessive forward tilt, which can cause sliding and hand pressure
- Avoid excessive backward tilt, which can cause lower back strain
For comprehensive saddle setup and comfort optimization, see our detailed Saddle Comfort Tips guide.
Adjusting Reach
The reach to your handlebars affects your comfort, breathing, and control of the bike. It's determined by stem length, handlebar type, and frame size.
Signs of Incorrect Reach
- Shoulder or neck pain
- Lower back pain
- Numbness in hands
- Difficulty controlling the bike
- Feeling cramped or overstretched
- Excessive weight on hands
- Poor handling at low speeds
Optimizing Reach
- Start with frame size
- Ensure proper frame stack and reach measurements
- Consider your torso and arm length
- Stem length adjustment
- Typical range: 70-120mm
- Shorter stems improve handling but may affect weight distribution
- Longer stems provide stability but can slow steering
- For detailed stem length calculations and optimization, see our Bike Stem Length Guide
- Handlebar selection
- Width should match shoulder width
- Consider reach and drop measurements
- Different shapes suit different riding styles
Warning
A reach that's too long can cause you to overstretch, while a reach that's too short can cause cramped positioning and reduced breathing capacity. Take time to find the right balance for your body proportions and riding style.
Handlebar Setup
Proper handlebar setup is crucial for control and comfort:
Width
- Match approximately to shoulder width
- Wider bars offer more control but less aerodynamics
- Narrower bars improve aerodynamics but may compromise handling
Height
- Higher position improves comfort and visibility
- Lower position reduces drag
- Consider flexibility and riding goals
Rotation
- Ensure drops are parallel to ground or slightly angled
- Brake lever position should allow comfortable access from both tops and drops
- Consider wrist angle in all hand positions
Cleat Position and Setup
Proper cleat setup is often overlooked but crucial for power transfer and comfort:
Fore/Aft Position
- Place cleats under the ball of your foot
- Can be adjusted slightly forward for more power
- Can be adjusted slightly back for more comfort
Rotation
- Start neutral (parallel to foot)
- Adjust based on natural foot rotation
- Watch for knee tracking during pedaling
Float
- Choose appropriate cleat float based on knee health and riding style
- More float can help prevent knee issues
- Less float can improve power transfer
Professional Bike Fitting
While basic adjustments can be made at home, a professional bike fitting can provide a more comprehensive analysis of your position on the bike.
What to Expect
Professional fittings typically include:
- Detailed body measurements
- Dynamic analysis of your pedaling
- Video analysis of your position
- Adjustments to all contact points
- Recommendations for component changes if needed
- Follow-up adjustments as needed
Types of Professional Fits
- Basic Fit (1-2 hours)
- Essential measurements and adjustments
- Good for beginners or casual riders
- Comprehensive Fit (2-3 hours)
- Detailed analysis and adjustments
- Video analysis
- Pedaling efficiency assessment
- Advanced Dynamic Fit (3-4 hours)
- Motion capture technology
- Pressure mapping
- Advanced biomechanical analysis
When to Get a Professional Fit
- When first getting serious about cycling
- After purchasing a new bike
- Following injury or surgery
- When training for a significant event
- If experiencing persistent discomfort
- When changing riding styles or disciplines
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Related Bike Fitting Tools & Calculators
Enhance your bike fitting process with our specialized calculators:
Essential Calculators
- Bike Size Calculator - Complete frame sizing based on height and inseam
- Saddle Size Calculator - Find your ideal saddle width and height
- Stem Length Calculator - Optimize reach and handling
Additional Resources
- Choosing the Right Bike Guide - Select the perfect bike type for your needs
- Saddle Comfort Tips - Advanced saddle setup and comfort optimization
Professional Services
Consider these services for advanced bike fitting:
- Basic Fit (1-2 hours) - Essential measurements and adjustments
- Comprehensive Fit (2-3 hours) - Detailed analysis with video review
- Dynamic Fit (3-4 hours) - Motion capture and biomechanical analysis
Common Fit-Related Issues and Solutions
Knee Pain
- Front knee pain: Often indicates saddle too low or too far forward
- Back knee pain: May suggest saddle too high or too far back
- Side knee pain: Could be related to cleat alignment
Back Pain
- Lower back pain: Often related to reach or saddle angle
- Upper back pain: May indicate excessive reach or high handlebar position
Hand Numbness
- Check handlebar height and reach
- Evaluate saddle position and angle
- Consider padded gloves or different bar tape
Foot Numbness
- Evaluate cleat position
- Check shoe fit and cleat tension
- Consider insoles or wider shoes
Conclusion
Proper bike fitting is essential for comfortable, efficient, and injury-free cycling. Using professional measurement techniques like the 109% inseam calculation method and maintaining optimal positioning will dramatically improve your riding experience. Remember that bike fit is an ongoing process—as your flexibility, strength, and riding style evolve, regular adjustments may be needed.
Key takeaways for perfect bike fit:
- Use precise measurements and calculations for saddle height
- Maintain 25-35° knee bend at bottom of pedal stroke
- Ensure proper weight distribution (60% rear, 40% front)
- Start with professional guidance when possible
- Make adjustments gradually and test thoroughly
For personalized bike sizing recommendations, use our comprehensive calculators:
- Complete Bike Size Calculator - Full frame sizing analysis
- Saddle Size Calculator - Personalized saddle measurements
- Stem Length Calculator - Optimal reach calculations
Professional Bike Fitting Recommendation
While this guide provides professional techniques for basic bike fitting, consider investing in a professional bike fit session for optimal results. A qualified bike fitter can identify issues you might miss and provide specialized solutions for your unique body mechanics and riding style.